Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMSIVND)
| Drug Name |
Hydroxychloroquine
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Hidroxicloroquina; Hidroxicloroquina [INN-Spanish]; Hydroxychlorochin; Gen-Hydroxychloroquine 200mg Tablets; HCQ; Hydroxychloroguine; Hydroxychloroquine (INN);Hydroxychloroquine [INN:BAN]; Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate (1:1) Salt; Hydroxychloroquinum; Hydroxychloroquinum [INN-Latin]; Idrossiclorochina; Idrossiclorochina [DCIT]; Oxichlorochinum; Oxichloroquine; Oxychlorochin; Oxychloroquine; Plaquenil (TN); Polirreumin; Polirreumin (TN); Quensyl; WIN 1258
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antimalarials
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Plasmodium
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
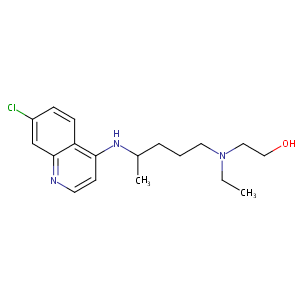 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 335.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Chronic renal failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | GB61.Z | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Hydroxychloroquine
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Hydroxychloroquine (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Hydroxychloroquine FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7198). | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04341727) Hydroxychloroquine,Hydroxychloroquine,Azithromycin in the Treatment of SARS CoV-2 Infection (WU352). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | TLR7/9 antagonists as therapeutics for immune-mediated inflammatory disorders. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2007 Dec;6(4):223-35. | ||||
| 9 | Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020 Mar;30(3):269-271. | ||||
| 10 | Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: implications for rheumatology. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;16(3):155-166. | ||||
| 11 | MDR-ABC transporters: biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013 Sep-Oct;31(5):779-87. | ||||
| 12 | Hydroxychloroquine: a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model in the context of cancer-related autophagy modulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Jun;365(3):447-459. | ||||
| 13 | Hydroxychloroquine decreases human MSC-derived osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Feb;22(2):873-882. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13373. Epub 2017 Oct 3. | ||||
| 14 | Attenuation of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine on the invasive potential of bladder cancer through targeting matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression. Environ Toxicol. 2021 Nov;36(11):2138-2145. doi: 10.1002/tox.23328. Epub 2021 Jul 19. | ||||
| 15 | Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization is a critical step of lysosome-initiated apoptosis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Oncogene. 2003 Jun 19;22(25):3927-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206622. | ||||
| 16 | Reactive oxygen species mediate chloroquine-induced expression of chemokines by human astroglial cells. Glia. 2004 Jul;47(1):9-20. doi: 10.1002/glia.20017. | ||||
| 17 | Hydroxychloroquine-inhibited dengue virus is associated with host defense machinery. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Mar;35(3):143-56. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0038. Epub 2014 Oct 16. | ||||
| 18 | Hydroxychloroquine potentiates Fas-mediated apoptosis of rheumatoid synoviocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Jun;144(3):503-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03070.x. | ||||
| 19 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 21 | Harper KM, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR "Vasopressin and alcohol: A multifaceted relationship." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235 (2018): 3363-79. [PMID: 32936259] | ||||
| 22 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 23 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 26 | Carrion C, Espinosa E, Herrero A, Garcia B "Possible vincristine-isoniazid interaction." Ann Pharmacother 29 (1995): 201. [PMID: 7756727] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
